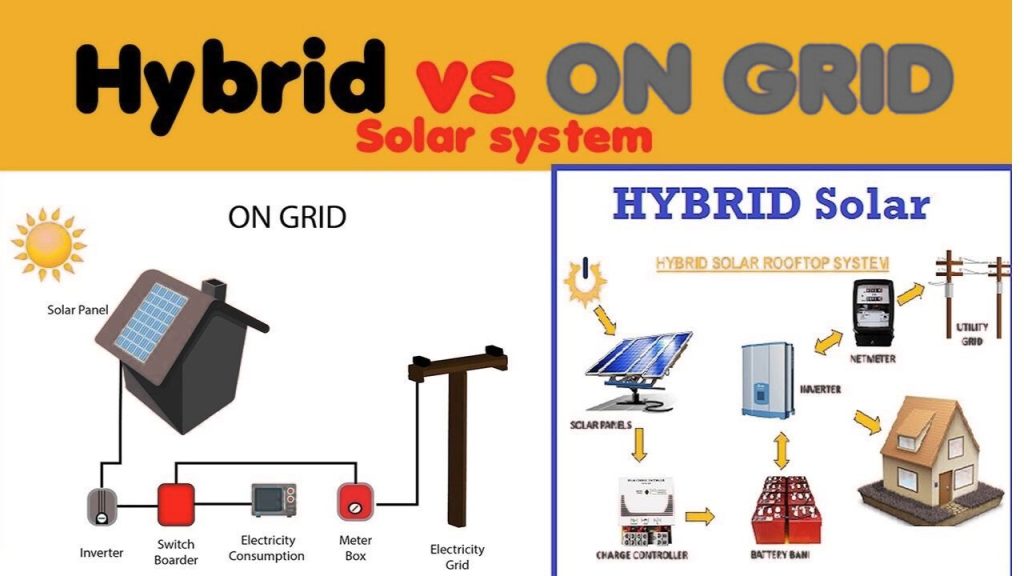
Difference between on grid and hybrid inverter
Difference between on grid and hybrid: Going to look to switch to solar power? Excellent decision! The problem is, solar panels are just one component of the whole picture. The inverter—the device that transforms sunlight into useful electricity—is where the real magic occurs. Now, the on-grid vs. hybrid inverter debate is likely anything that you have encountered while researching inverters. Which are you in need of? For what reason is it important? To help you choose the best option for your house or place of business, let’s distill something into a simplified way.
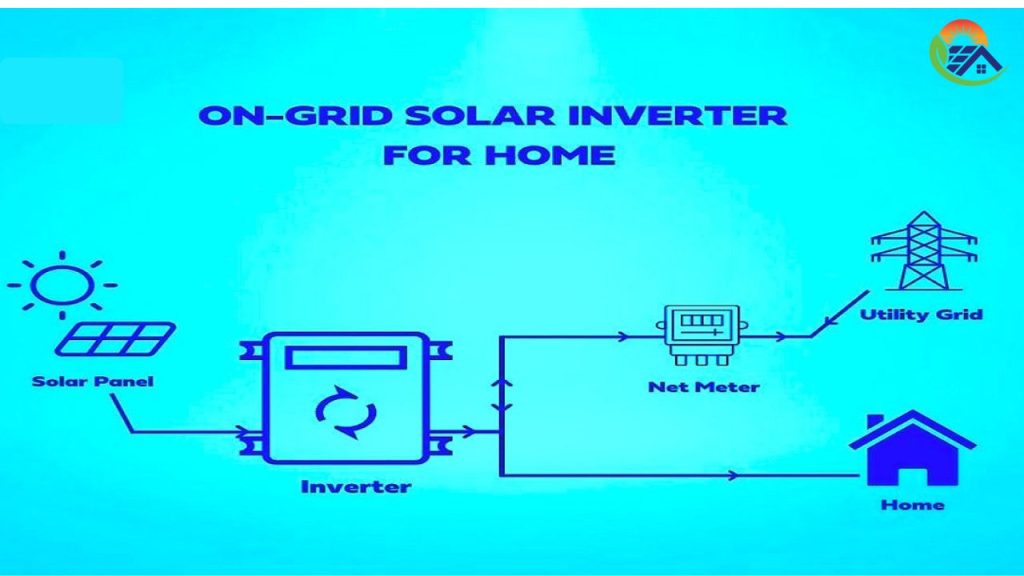
What is an On-Grid Inverter?
An on-grid inverter, as well known as a grid-tied inverter, is similar to a solar system’s social butterfly. To power your house, it cooperates with the utility grid in your neighborhood. This is how it ends up going:
- How It Works: Produces AC electricity for your house from solar DC power. Any extended vitality? Net metering credits are used to feed it back into the grid.
- Important attributes:
- Grid-Dependent: Turns off during shutdowns to uphold utility workers (first and above all, safety!).
- Batteries really aren’t required: use the grid as a backup, that also lowers expenditures.
- Net Metering Friendly: Sell extra energy to the grid to earn credits.
- Ideal For: Homes with trusted grid access in urban or suburban areas. Contemplate it as an outlay partner for reducing electricity costs.
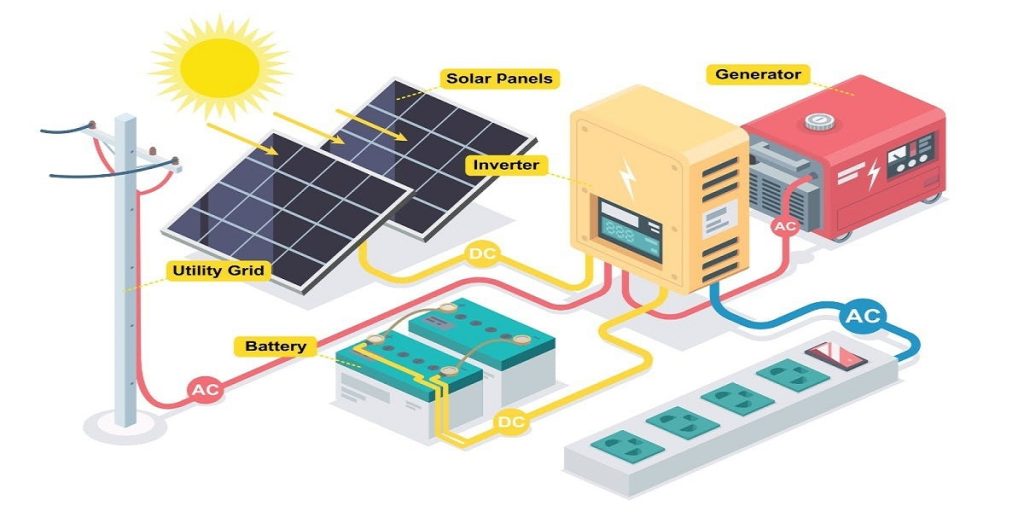
What is a Hybrid Inverter?
An all hybrid inverter is the solar pv equal of a Swiss Army knife. Grid connectivity and battery storage are combined to provide the best of both worlds. Notable benefit include:
- Compatibility with battery pack: Stores extra solar energy for use at a later time (think at night or on overcast days).
- Grid independence: Able to work independently in the event of a power outage, eradicating disruptions to Netflix.
- Future-ready: Easily integrates future solar panels or additional batteries.
Ideal for: People who abhor losing power during storms, eco-conscious persons who want to become self-sustainable, and rural areas with erratic grid reliability.
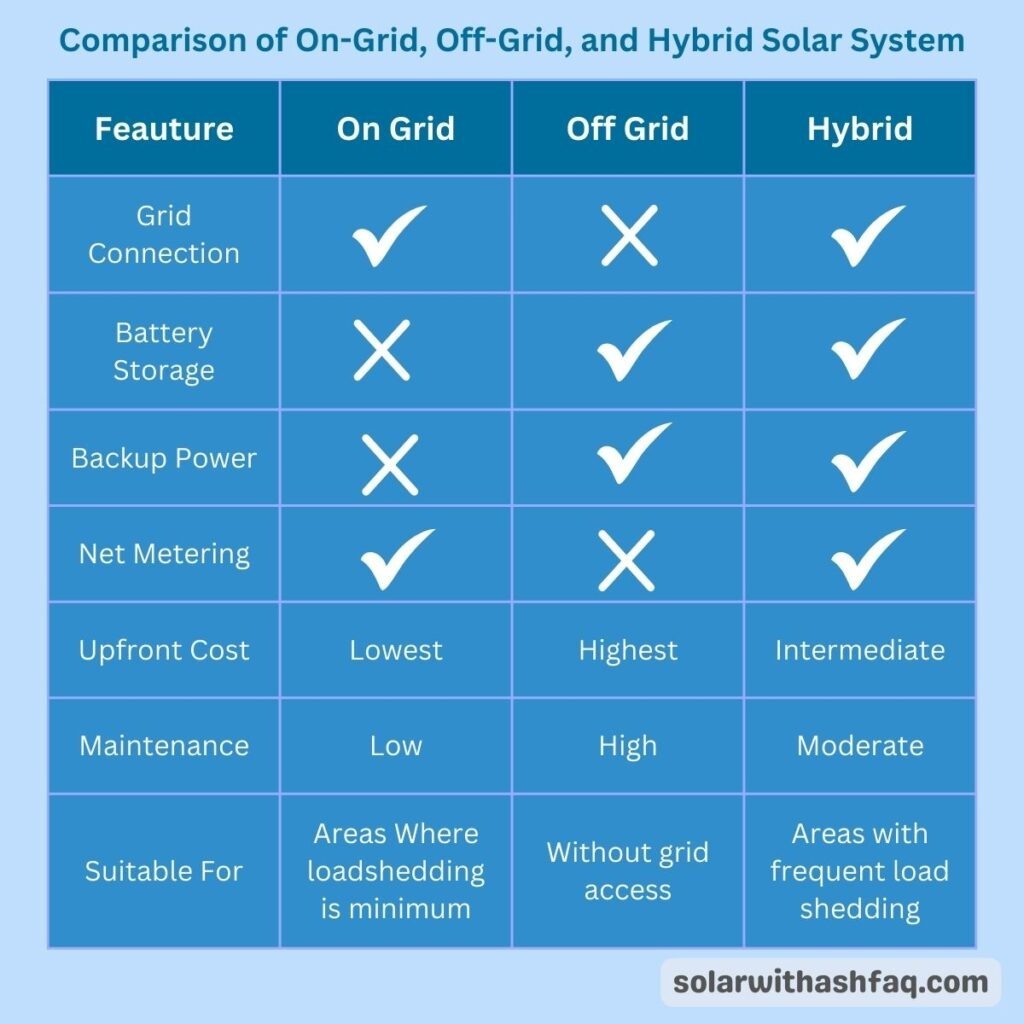
Quick Comparison: Difference between on grid and hybrid inverter
| Feature | On-Grid Inverter | Hybrid Inverter |
| Grid Connection | Required to function | Works with or without grid |
| Battery Support | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Backup Power | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Upfront Cost | Lower | Higher (batteries add cost) |
| Complexity | Simple setup | More advanced installation |
| Energy Independence | Low | High |
Key Difference between on grid and hybrid inverter
Grid Reliance:
- During outages, on-grid inverters turn off to safeguard utility employees (safety first!). The grid is necessary for them to function.
- When the grid fails, hybrid inverters switch to battery power so your lights stay on.
Storage of Batteries:
- Energy cannot be stored by on-grid systems; instead, the grid serves as a “virtual battery.”
- With hybrid systems, you can prepare for rainy days by storing solar energy like a squirrel does with acorns.
Cost Factors:
- On-grid inverters are more cost-effective. Lower initial investment if there are no batteries.
- Because of batteries, hybrid systems are more expensive up front, but they are more resilient and save money over time.
Scalability
- The flexibility of hybrid inverters is greater. Later on, do you want to add more panels or batteries? No issue.
- Although on-grid systems are easier to use, they are less flexible if your energy requirements increase.
Advantages and Disadvantages of on grid and hybrid inverter
On-Grid Inverter
- Advantages: Low cost, simple setup, benefits of net metering.
- Disadvantage: No backup power, meaning it’s worthless during blackouts.
hybrid inverter
- Advantages: Future upgrades, blackout protection, and energy storage.
- Disadvantages: provide a somewhat steeper learning curve and a higher initial cost.
FAQs
Q: Can I subsequently add batteries to an on-grid inverter?
A: hybrid inverter or additional equipment (such as a DC coupler) would be required, but technically yes. Hybrids are frequently less expensive to start with.
Q: Do hybrid inverters function when there is a blackout?
A: Definitely! Candlelight dinners are out of the question (unless you’re into that). They automatically switch to battery mode.
Q: What is the more economical option in the long run?
A: If outages occur frequently or energy prices rise, hybrid inverters save money. Where the grid is reliable and affordable, on-grid works best.
conclusion
Difference between on grid and hybrid inverter: Your priorities will determine whether you choose a hybrid or on-grid inverter: resilience vs. cost. Go on-grid if you want to save money right away and are grid-happy. Hybrids are worth the investment if you frequently experience outages or long for energy independence.
Are you prepared to embrace solar energy? To customize a system to your requirements, speak with a local specialist. Then, take pleasure in the assurance that comes with clean, dependable energy.